
What is the Metaverse?
Is the metaverse the future? From Mark Zuckerberg changing the name of Facebook to Meta, to games that generate various incomes for their users, the metaverse seems to be the future of how we interact with each other.

If you have recently followed Bitcoin closely, or perhaps have followed other social media related to cryptocurrencies, most likely you’ve heard or read more than once the term Blockchain.
Blockchain, is the technology behind Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
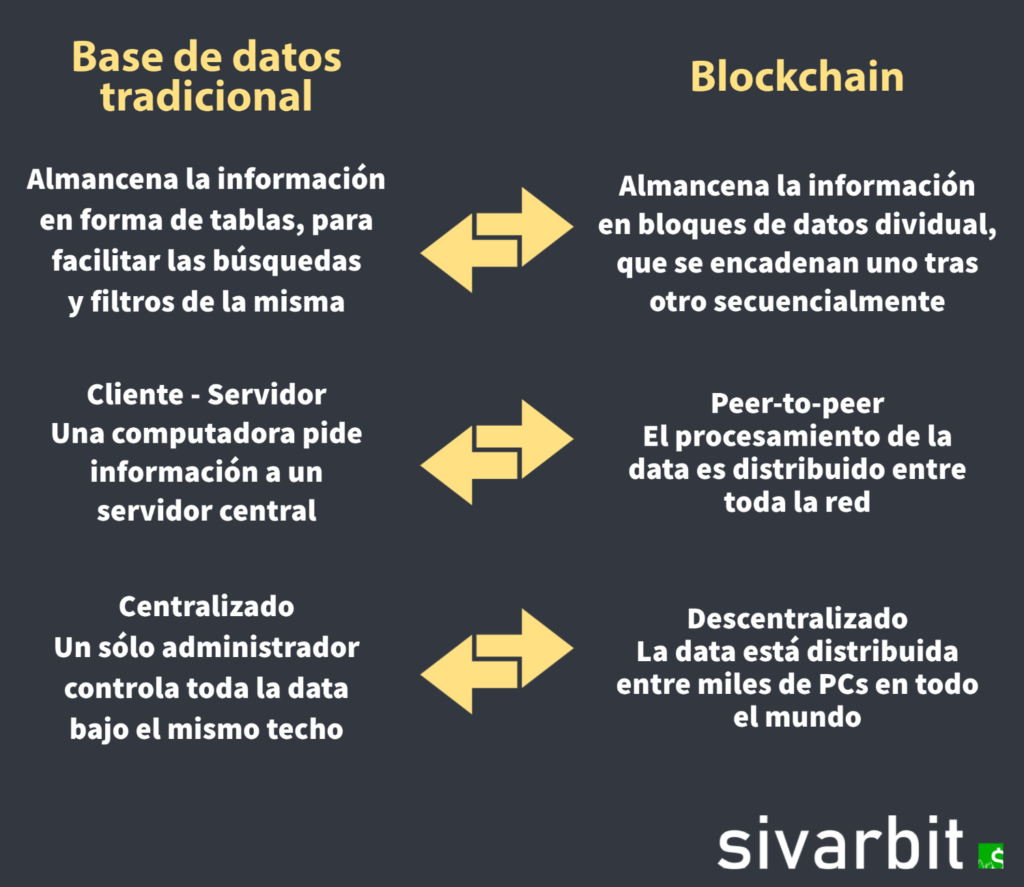
The Blockchain, in simple terms, is a database. There are many types of databases, from a simple spreadsheet in Excel, to more complex databases such as SQL and Oracle, the latter used by large corporations around the world.
In the blockchain, data is stored in information chunks, and each of these is known as “Block”. Each block has a maximum capacity to store data, and when that limit is reached, that block is chained to the previous block, thus extending the chain itself.
A block has a unique code that identifies it, known in English as “hash”. Each block contains the previous hash, its own hash and a timestamp.
You can think of the hash as that very important Excel file that you store on your computer, and that identifies it among other files.
Fuente: El Canal de Shackra│Canal de YouTube │Adaptación del video original de weusecoins.com
There are three main features that make the Blockchain a unique technology. These three pillars are decentralization, transparency and security.
To understand this better, imagine a company that owns a database of banking transactions with 1000 computers in it, all located under one roof. Although any authorized person can access the database from anywhere in the world, thanks to the internet, all the data is controlled by the same entity, the same computer program, and usually in one place, although this can vary.
A Blockchain however, may have 1000 computers in it, or more, but most of them are distributed between nodes or completely independent entities, located in different geographical areas.
This means, no one is the authority, the authority are all nodes in the network, and if one has incorrect information, it will use all the other nodes in the network as a reference, to correct its own copy of the transaction book, known as ledger.
This part is key, as no one can manipulate the data at will, since the data is and always will be the record of historical data that occurred, of which all have copies.
Later we will discuss uses of the blockchain beyond Bitcoin and cryptocurrencies, and then we will realize how the principle of decentralization is a perfect setting for public systems, such as the electoral or health system.
Now that we have understood how the Blockchain is a decentralized database, we can clearly see how this technology generates transparency.
Historical data in the chain itself can be viewed at any time, by any node or computer that is part of the network, or even anyone outside of it, via Blockchain explorers.
If you want to know the most recognized Blockchains explorers, you can click here.
Anyone can track the movements of Bitcoin from the beginning of its history to the present, since the information is accessible to everyone, and that is why it is transparent.
Now, it is important to understand that anonymity is a key part of this technology, so knowing who sent and received Bitcoin is much more difficult, because the only public information is the alphanumeric address of the “wallet”, from where it is sent and who received that Bitcoin, but the identity of the individuals is protected.
It would take a much deeper research effort and lots of cooperation, to discover who are the individuals who interacted in a transaction.
The Blockchain stores data that can not be lost, modified or deleted.
Security of stored information is one of the biggest benefits of Blockchain technology. If someone or a group of people would try to “hack” the network, duplicate transactions or modify the information, they would have to attack at least 51% of the other nodes in the network.
To carry out such an attack, the hacker would have to change its own copy of the ledger, but this would make the other nodes with the correct copy aware, which would give away this compromised node automatically, as illegitimate for the network
The amount of computational resources and money needed to carry out this attack are virtually impossible, as they would have to redo all the blocks, because now the hash marks and timestamps have changed. And even if for some reason remote this attack was successful, the network would notice the altering the blocks quickly enough, and so a “fork off” would happen, which would create a new version of the chain that has not been affected, causing the other one to lose intrinsic value, and thus eliminating the very same reason for the attack.

The financial sector has been the sector that has adopted Blockchain the fastest, although they are the first to feel threatened by it. In finance, the Blockchain solves security problems, accessibility to information by customers themselves, transaction costs, speed of global transactions, among others. On top of this, the blockchain does not close, it can operate 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, since it does not depend only on one entity, but on several.
The healthcare sector could benefit a lot from the Blockchain. All medical records generated from the public and private sector, may be stored sequentially in the blocks of the chain. The information of each patient would be safe, but globally accessible to any authorized entity, and could not be altered or falsifiable. All these medical records may have their own private key or password, so that they are only accessible by the patient or authorized parties.
Smart contracts are a decentralized computer program that will ensure a more transparent negotiation between the entities that participate in it, and its compliance is verified by the network itself. The benefit of these contracts is that they can be designed so that certain actions in the contracts occur as a result of specific conditions that are met or not. There is no way to alter these contracts, so what was traded is gold, and neither party loses.
Reforming electoral systems by occupying the Blockchain has the potential to eliminate fraud. A vote would be a piece of data, which would be part of a block, chained to the previous block in the chain. Remember, for a person or group of people to alter the votes they need to win, they will have to control and alter the copies of at least 51% of the nodes on the network itself, which, as we mentioned above, is virtually impossible, And if tried, the entire network would quickly realize it, as multiple existing copies would change, which goes against the very nature of the Blockchain.
Blockchain technology was first proposed in 1991. 20 years later, it has gained importance through Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. The rest of the financial sector is already beginning to develop their own technologies. There is a long way before the rest of the sectors in society and the economy begin to use Blockchain as a central technology, as change is always difficult for humans.
Now it is worth saying that this technology is here to stay, and there are many who said in 1990 that the internet was a fad or a technology that would not work. Others did not believe that Elon Musk and Tesla could succeed in creating something sustainable. Blockchain has many different uses that would help to modernize and democratize the way we live, therefore it is only a matter of time before the adoption rate continues to rise around the world.

Is the metaverse the future? From Mark Zuckerberg changing the name of Facebook to Meta, to games that generate various incomes for their users, the metaverse seems to be the future of how we interact with each other.

Just as in the world of stocks there are IPOs, also in the world of cryptocurrencies, new projects raise funds through ICOs.
