
What is Tether USDT?
Tether (USDT) is the largest stablecoin on the market by market capitalization, but is facing increasing competition from other stablecoins.

Ethereum is a digital platform based on the same technology behind Bitcoin, The Blockchain, but with notable differences. This platform has its own cryptocurrency called Ether (ETH), and its own programming language called Solidity.
The main objective of the creation of Ethereum was not to become a digital currency, rather, to serve as a base platform for the development of smart contracts and decentralized applications (Daaps).
Do you want to know more about smart contracts and Dapps? Click here.
Fuente: El Canal de Shackra│Canal de YouTube │Adaptación del video original de weusecoins.com
Ethereum was born with the objective of providing developers with a platform to create, develop, launch and monetize smart contracts and decentralized applications. This would be possible using the programming language called Solidity, native to Ethereum, and running these applications on the platform itself, thus minimizing the risk of network outages, fraud and third-party interventions.
Ethereum was founded in July 2015 mainly by Joseph Lubin and Vitalik Buterin. Buterin is the best-known face in the environment, and is credited with creating the concept of Ethereum. He serves as the CEO and public face of the platform.
Like Bitcoin, Etheurem works by storing transactions or data through blocks that connect to previous blocks in the chain.
Ethereum operates in a decentralized manner, through computers or independent nodes that are part of the network itself, and in turn verify the validity of transactions, using the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), the brain of Ethereum.
These independent nodes, which at the same time are miners, put their computational power to verify transactions and create blocks, and through the proof-of-work (PoW), that is, to successfully solve mathematical operations to check transactions and discover another block, they receive Ether (EHT) as compensation.
Do you want to know what a miner is? We will explain it to you here.
In the case of Ethereum, there is an important concept to introduce, which does not exist in Bitcoin. This is the concept of Gas.

Yes, it sounds like the gasoline you put in your car, but here we explain to you what this refers to.
Gas is a fee part of the Ethereum network, which represents the cost required to process a transaction or execute a contract.
These gas fees are the biggest criticism that Ethereum has had and continues to have throughout its history, since it is sometimes quite expensive to carry out transactions for those who operate in this network.
This is the reason why second layer protocols have been born, such as Polygon (MATIC), this being the most important. These protocols allow operating under fees almost close to 0 dollars per transaction.
If you want to know more about Polygon (MATIC), click here.
The value of gas is given in fractions of Ether (ETH), and is established by the miners themselves, in reference to supply and demand. Commonly this small fraction of the coin is known as Gwei.
As an example, the cost of processing a transaction within a contract could be 1/100,000 ETH
Ethereum miners, as a reward for executing all verification and transaction processing tasks within the network, receive this fee. Miners can decline to carry out a transaction if the value of the fee is too low.
If you want to know what the gas value is in real time, you can visit this page:
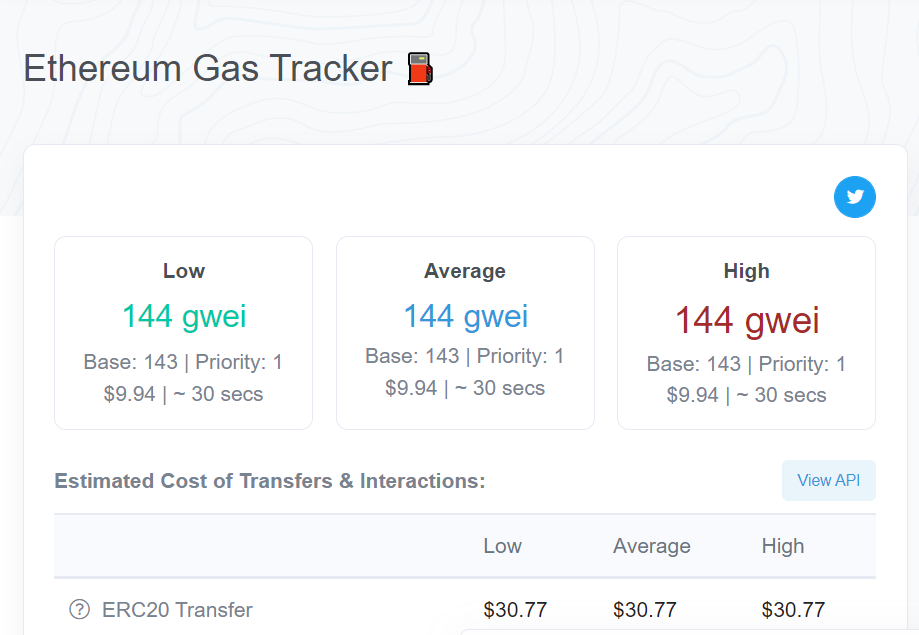
Blockchain technology promises security against attacks and hackers. This is due to its decentralized structure and verification of transactions through blocks.
Contrary to the statement above, in 2016 an attacker stole more than $50 million worth of Ether, which had been raised for a project called DAO. This project was created based on Ethereum technology, for smart contracts, by a third party, not the creators of Ethereum.
The reason for this theft of ETH was due to vulnerabilities in the DAO project base code, which had already been exposed by experts in the field, but were not corrected in time.
After much debate in the Ethereum community, it was decided to carry out a Hard Fork, which meant making changes to the network’s operating protocols.
This change introduced Ethereum 2.0
While the vast majority of stakeholders embraced the change and the fork was implemented, not all agreed. Consequently, the hard fork resulted in two competing, and now separate Ethereum blockchains.
Those who refused to accept the fork that rolled back the blockchain history, supported the pre-forked version, now known as Ethereum Classic (ETC).
The blockchain currently known as Ethereum, is the blockchain that implemented the hard fork and altered the history of the network, and the history of the blockchain as a whole.
Ethereum, unlike Bitcoin, was not created with the sole purpose of offering a decentralized digital currency system, rather, to offer a decentralized platform for the development of decentralized applications and smart contracts, which had its own payment system for the execution of transactions, via ETH.
Some of the main differences between both platforms are:
As we mentioned before, Ether is the second largest cryptocurrency in market value, and still is the most widely used ecosystem to start new decentralized projects.
2022 will be a very important year for Ethereum, as this blockchain will go through its most important change in a long time, transforming to ETH2.
This transformation will make Ethereum more scalable, secure, and sustainable. Fundamentally, Ethereum will go from being a Proof-of-Work blockchain, to a Proof-of-Stake blockchain (PoS).
This will bring the number of transactions the network can handle per second, to hundreds of thousands, and will eliminate the high electricity costs for miners, as well as the painful gas fees for its users. The nodes will no longer be miners, but their participation in transaction verification will depend on how much Ether they own, demonstrating their commitment to the ecosystem itself.
The more Ether (ETH) the node stakes, the more possibilities it will have to win the raffle to verify new blocks, and thus the more ETH it will earn as reward.
Yes, just as you can buy Bitcoin, you can buy Ethereum. To do this, you need to register with a cryptocurrency exchange or open a self-custody wallet.
As the second cryptocurrency with the highest market value, many exchanges will allow you to buy ETH directly with your dollars or local currency. If not, it is quite easy to buy Bitcoin first, and convert to ETH later. The fee for this conversion varies by exchange, but they are relatively low.
Remember that just like investing in Bitcoin, investing in Ether is speculative and risky, and nothing and no one can assure you the success of your investment. Never invest money that you are not willing to lose. That will let you sleep peacefully at night, as remember that the cryptocurrency market never closes.

Tether (USDT) is the largest stablecoin on the market by market capitalization, but is facing increasing competition from other stablecoins.

NFTs are perhaps one of the most exciting creations that the blockchain has brought about, and their potential goes far beyond collectible jpegs.
